- P.vivax Causes 43% of all cases of malaria in the world.
- P. vivax was found mainly in the United States, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa.
- Plasmodium vivax does not infect West Africans due to the fact that West Africans do not possess the Duffy Antigen on the red blood cells which the parasite requires to enter the red blood cell.
- It has an incubation period of between 10 and 17 days which is sometimes prolonged to months or years due to the formation of hypnozoites .
- It has a periodicity of 48 hours.
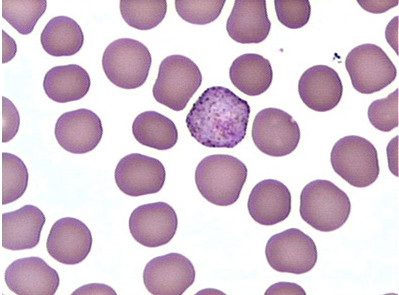
- Plasmodium vivax infections are usually characterized by the presence of more than one developmental stage in the peripheral blood film.
- The parasites parasitize young enlarged erythrocytes and Schüffner’s dots develop on the erythrocyte membrane.
- The degree of infectivity is low, only the young immature corpuscles are infected; about 2% of erythrocytes are parasitized .
Morphology
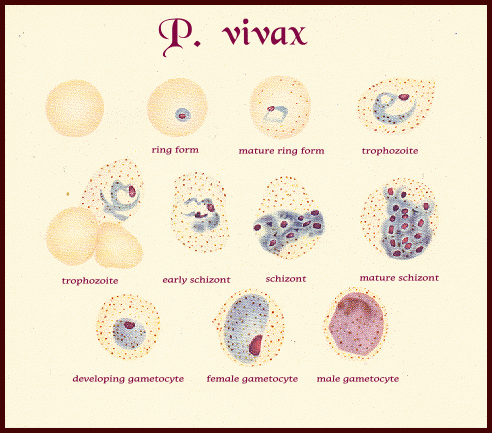
Trophozoites
- Most trophozoites of P. vivax are already several hours old when they appear in peripheral blood and by that time the Schüffner’s dots are already visible.
- As the trophozoites mature, the Schüffner’s dots increase in number and size.
shizont
- The parasitized red cells are much enlarged containing Schüffner’s dots. The parasites are large, filling the enlarged red cell.
- There are between 12-24 merozoites in the schizonts (usually16).
- The pigment is a golden brown central loose mass.
Gametocytes
- Mature female gametocytes are large rounded parasites which fill or nearly fill the host cell ,cytoplasm is blue and fairly homogenous.
- Mature male gametocytes can be distinguished from females by the large, loose and ill-defined mass of chromatin and by their paler color and smaller mass.
references :
www.atlas.or.kr
DIAGNOSING MEDICALPARASITES:A Public Health Officers Guideto Assisting Laboratory andMedical Officers